ASCO Highlights: Survivorship and Quality of Life After Breast Cancer | Breast Cancer Research Foundation
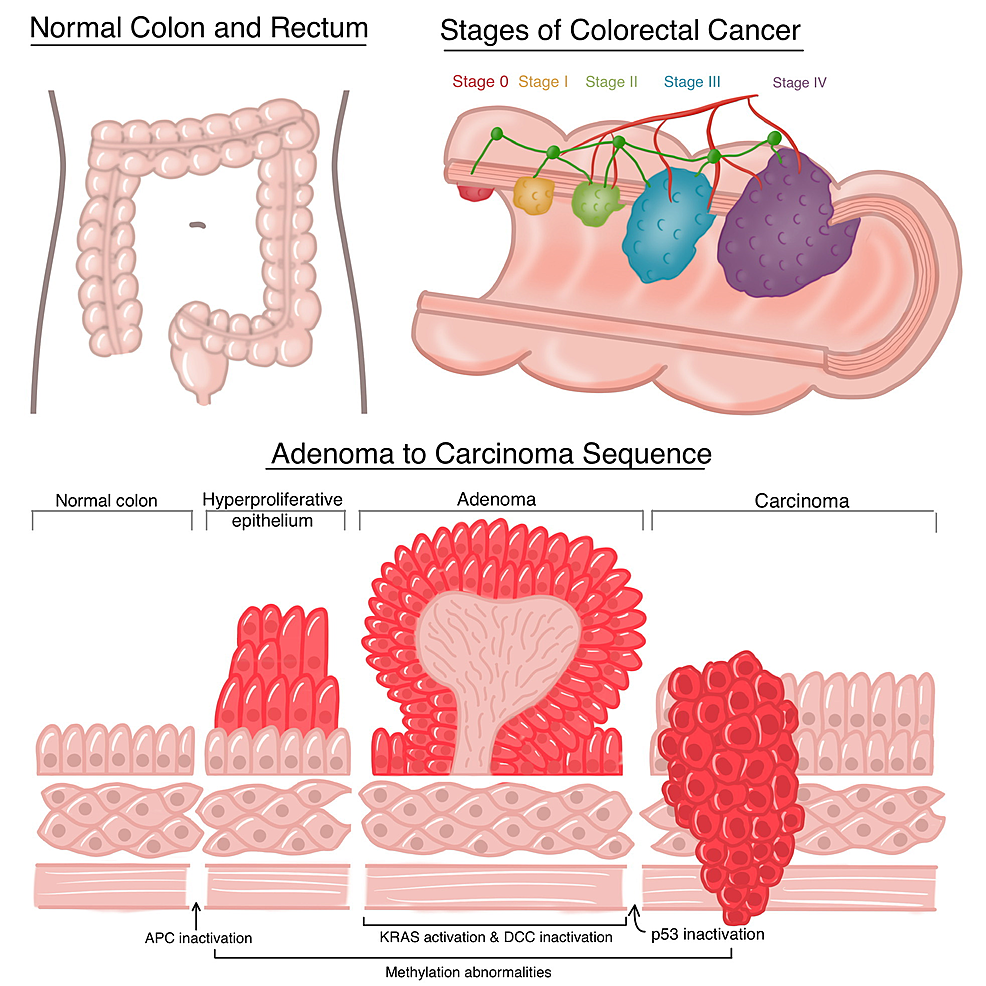
Cureus | The Role of Glucosamine and Chondroitin Sulfate in the Prevention of Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review | Article

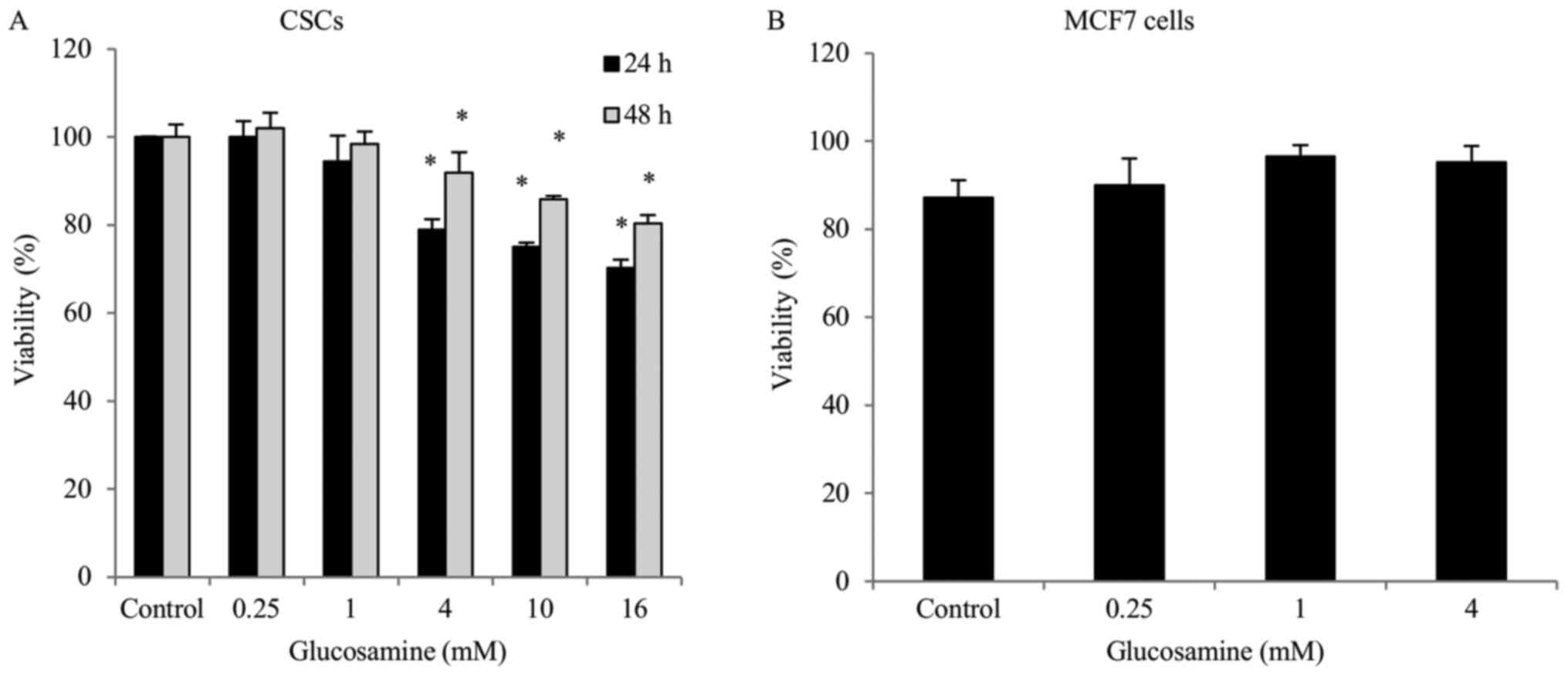
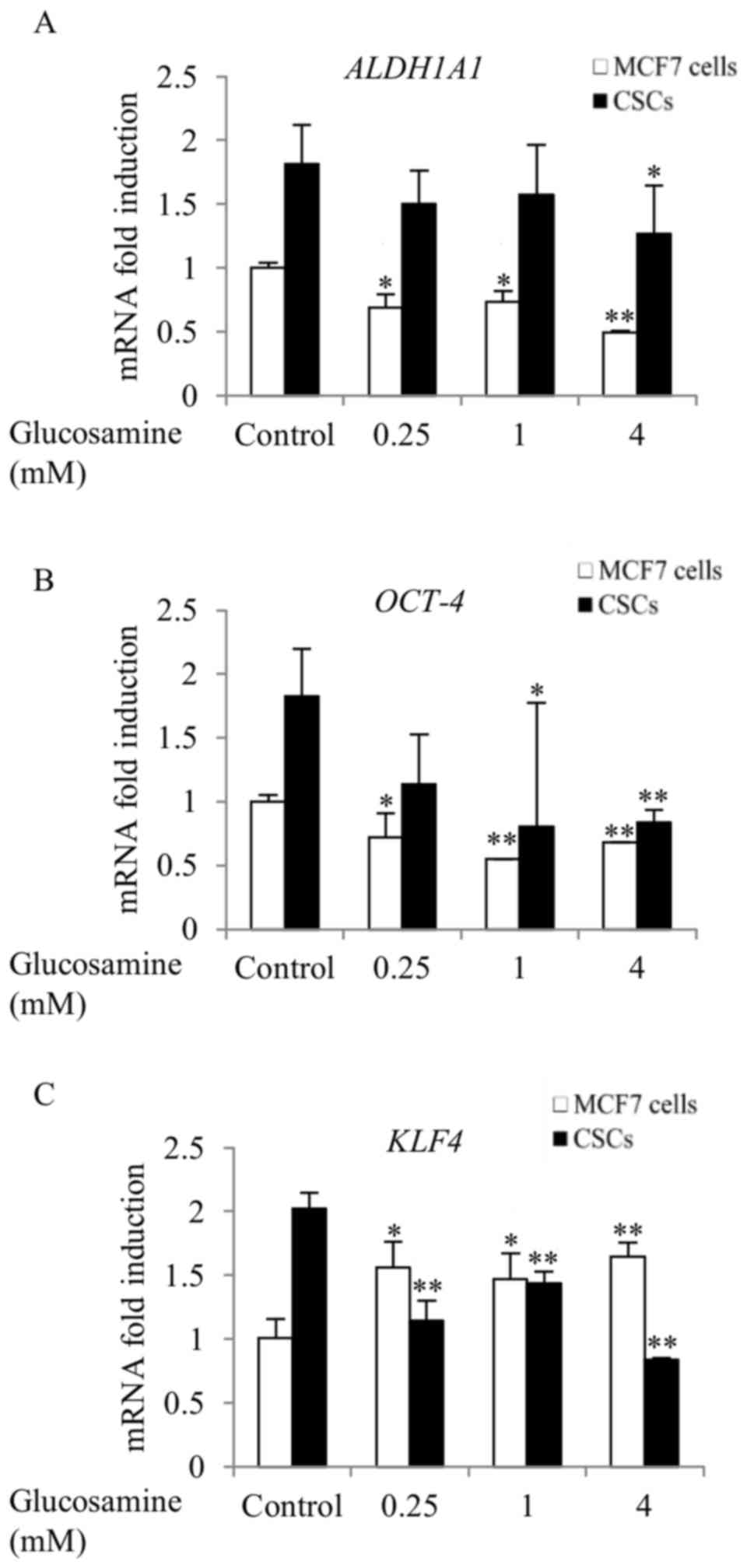
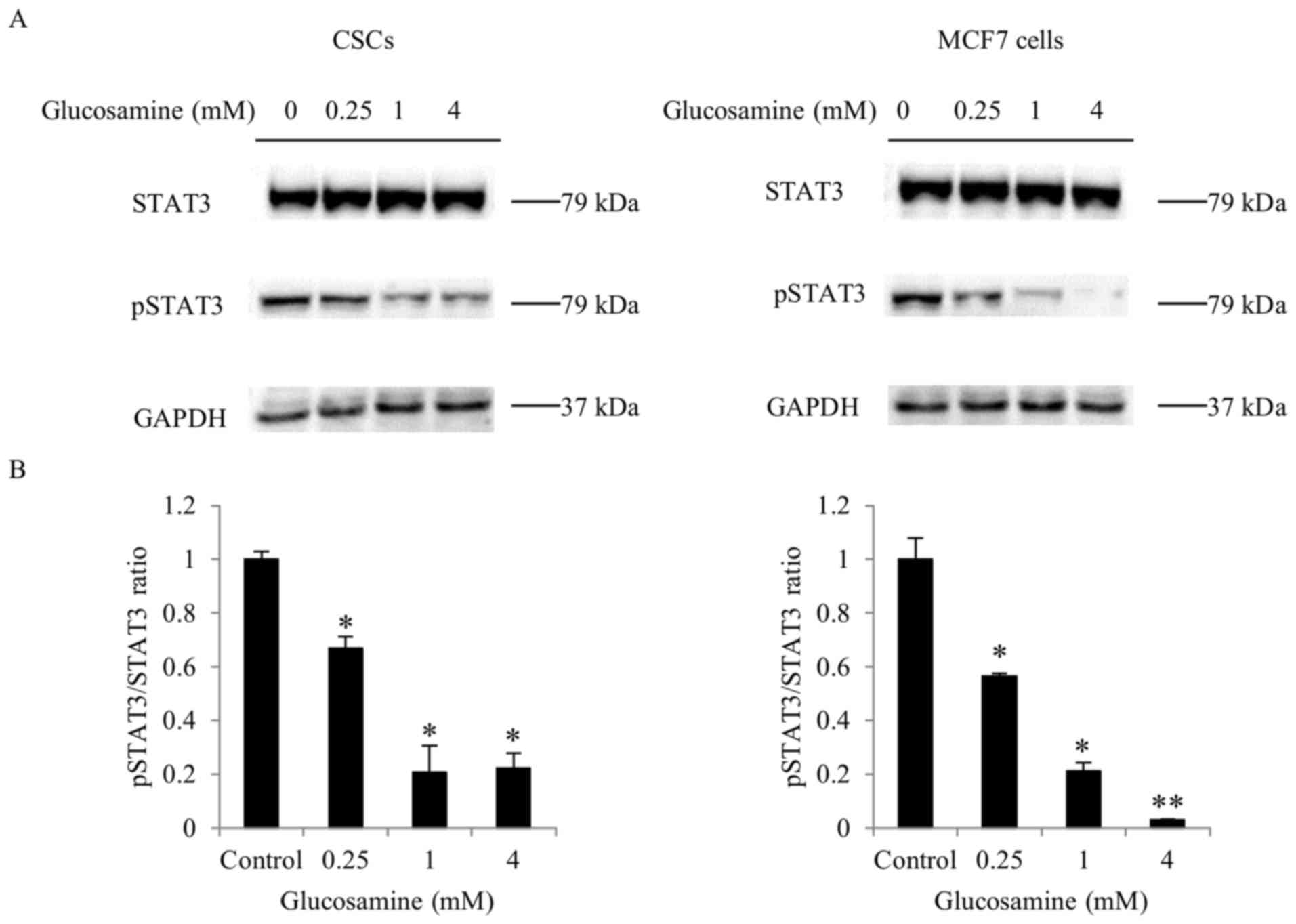
PDF) Glucosamine decreases the stemness of human ALDH+ breast cancer stem cells by inactivating STAT3

Glucosamine-conjugated graphene quantum dots as versatile and pH-sensitive nanocarriers for enhanced delivery of curcumin targeting to breast cancer - ScienceDirect
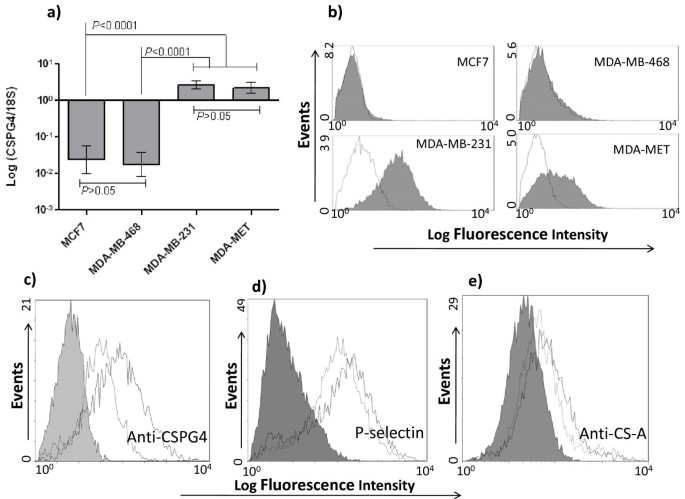
Chondroitin sulfates play a major role in breast cancer metastasis: a role for CSPG4 and CHST11gene expression in forming surface P-selectin ligands in aggressive breast cancer cells | Breast Cancer Research

Folate/N-acetyl glucosamine conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeting breast cancer cells: A comparative study. | Semantic Scholar
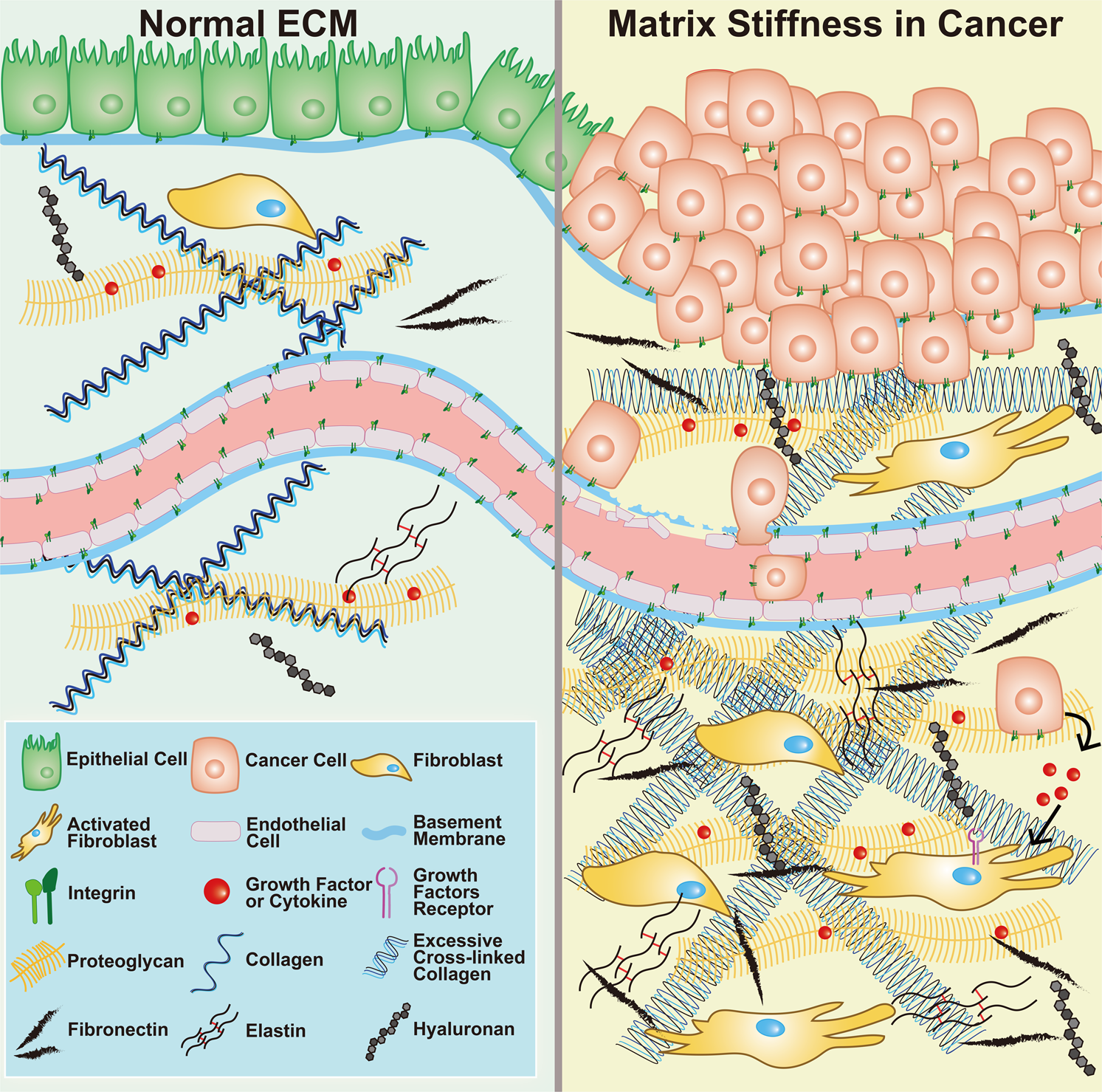
Extracellular matrix and its therapeutic potential for cancer treatment | Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy

Schematic representation of heparin and heparin conjugates action in... | Download Scientific Diagram

N-acetyl-d-glucosamine decorated nano-lipid-based carriers as theranostics module for targeted anti-cancer drug delivery - ScienceDirect
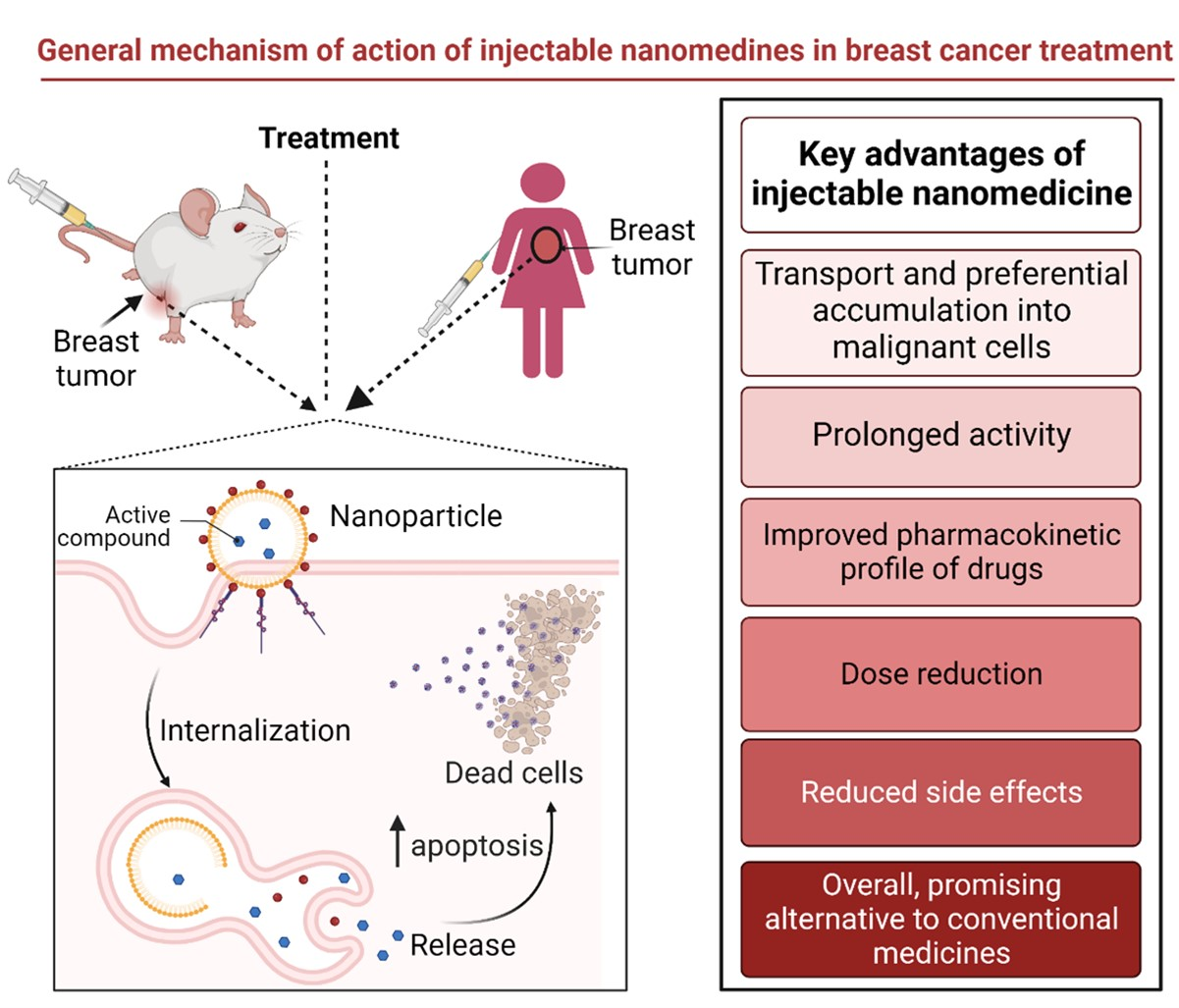
Pharmaceutics | Free Full-Text | Injectable Nano Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Breast Cancer

Folate/N-acetyl glucosamine conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeting breast cancer cells: A comparative study. | Semantic Scholar
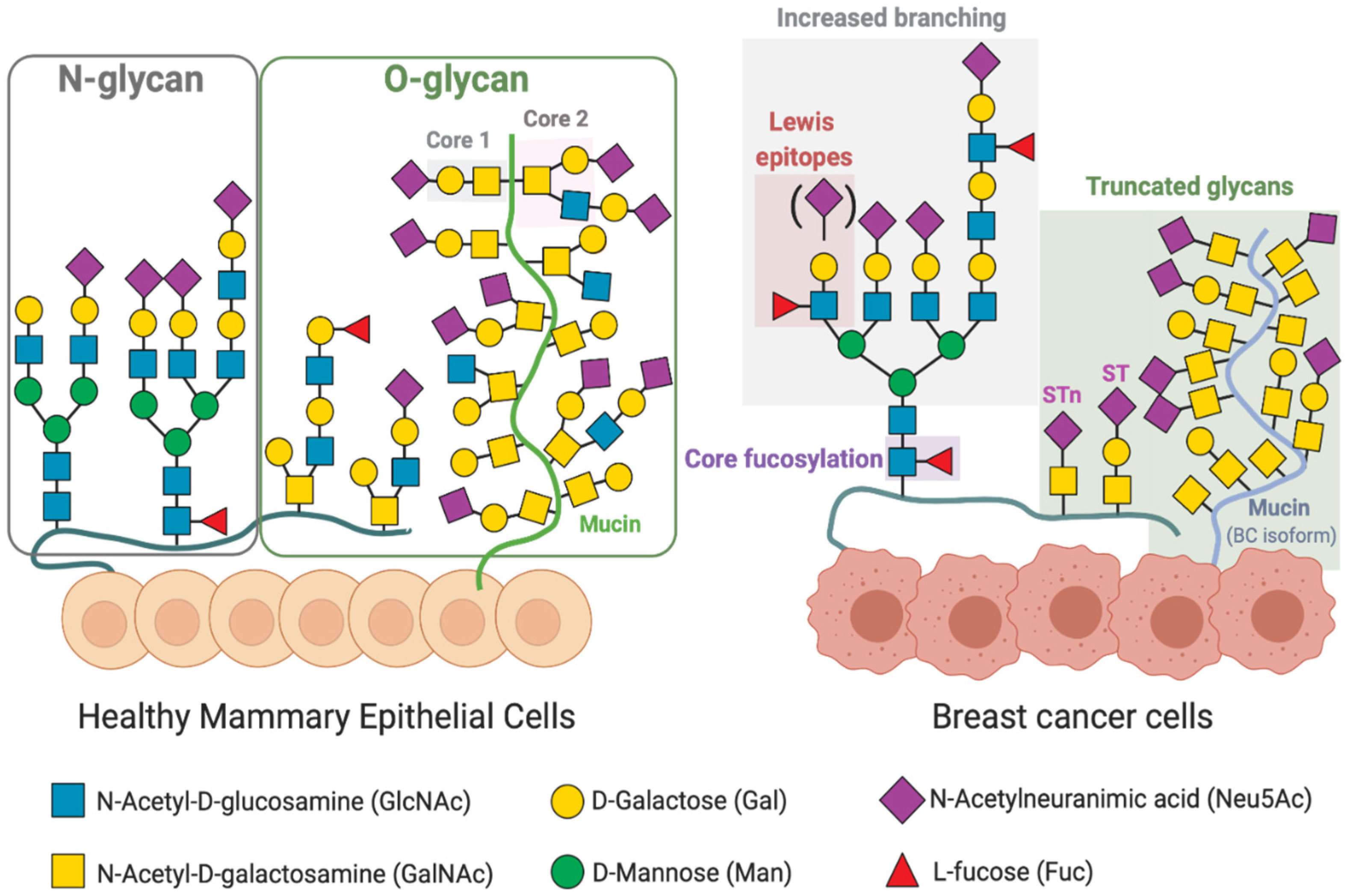
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Cracking the Breast Cancer Glyco-Code through Glycan-Lectin Interactions: Targeting Immunosuppressive Macrophages

PDF) Glucosamine decreases the stemness of human ALDH+ breast cancer stem cells by inactivating STAT3
Cracking the Breast Cancer Glyco-Code through Glycan-Lectin Interactions: Targeting Immunosuppressive Macrophages

Evidence-based approaches for the management of side-effects of adjuvant endocrine therapy in patients with breast cancer - The Lancet Oncology
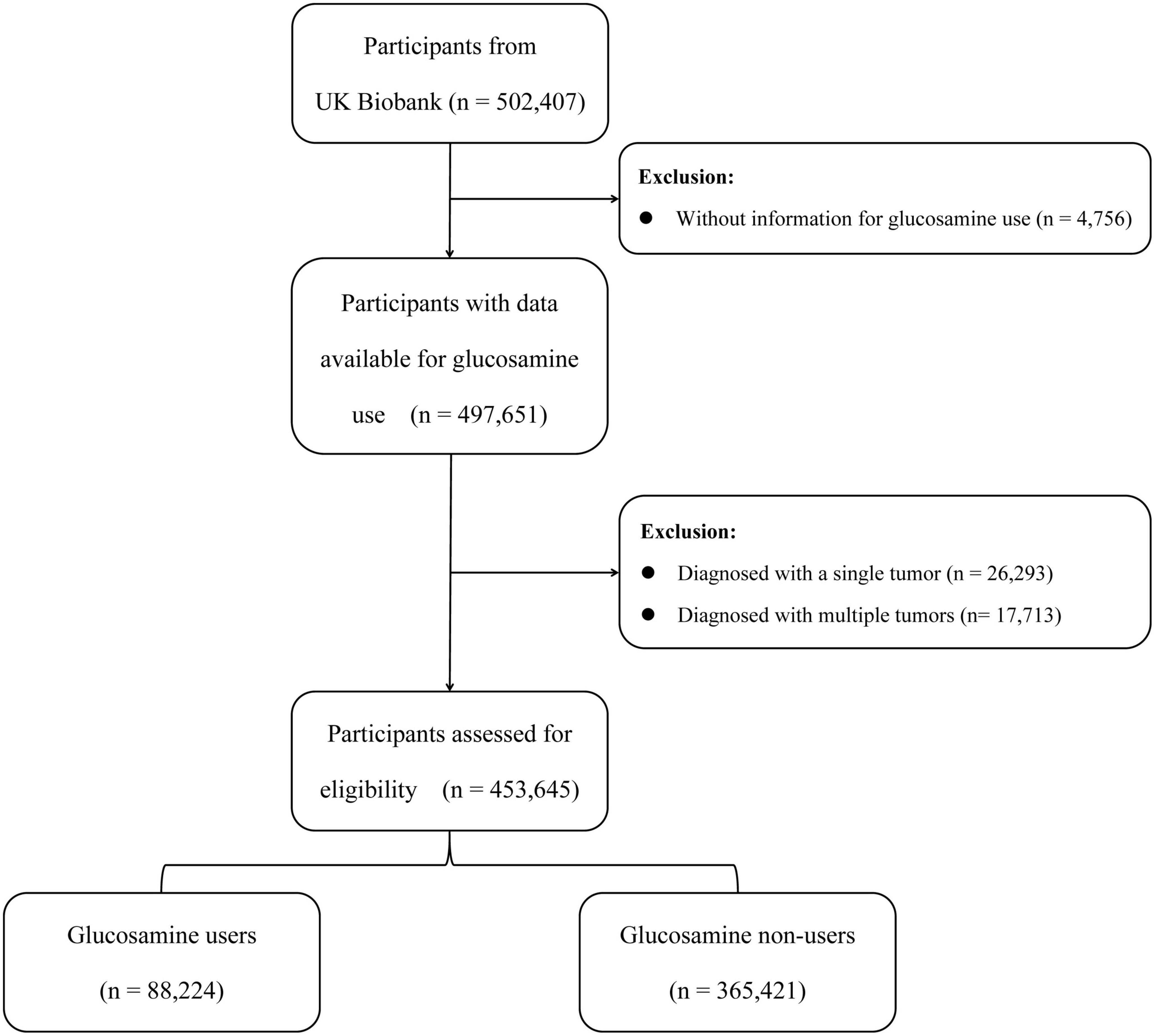
Frontiers | Association between glucosamine use and cancer mortality: A large prospective cohort study